Time Dilation??
Check out my demo! Featuring my pet rock: Rocky as the great big mass that warps spacetime!!
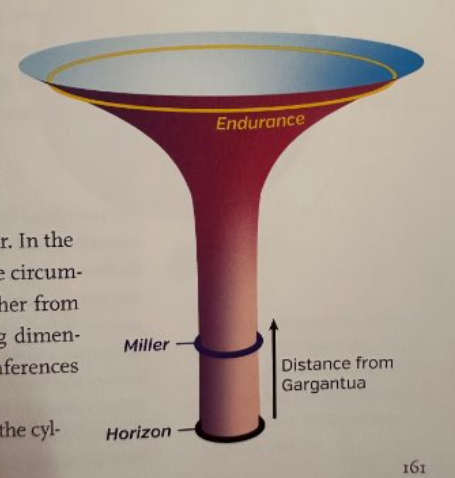
The space inside a black hole spins faster and faster the closer you get to the Event Horizon, and as the spin increases so does the slowing of time relative to an observer beyond Gargantua's gravitational influence. This diagram shows the increasing spin and corresponding decrease in the rate of flow of time.
This is a depiction of the warped space and time around a rapidly spinning black hole: one that spins at 99.8 percent of the maximum possible rate.
The bottom arrow of the diagram points to the Event Horizon where the spin is so great that time stops entirely relative to an outside observer.
There are three aspects of spacetime warping: the warp of space, the slowing and distortion of time, and the whirl of space. According to Einstein's theories of relativity, space and time are intrinsically connected. Because of this, the intense spin of space in a black hole will affect the flow of time.
We've been taught about how the motion of space around a mass is downwards towards it, but when the mass is as incredibly dense as a black hole, the fabric of space is stretched and that stretching is the time side of spacetime.
The diagram above shows a very good visual depiction of how spacetime would bend as a 2D form, and it aids our understanding of how it spacetime operates in coorelation to a black hole's overwhelming mass. However we must remember that spacetime is 4D, meaning that the warping of it is not just on a 2D level. This is a depiction of how that may look in the 3D sense. We can see an object with mass warping the space around it. This is in fact how gravity works and why it works all around us. No matter where you are on the planet, the spacetime is warped and pushing you (rather than pulling you) onto the planets surface.